An intuitive interface and safety are the top priorities for today’s Medical device designers. Functionality and aesthetics both play a crucial role in making a device user-friendly.
A John Hopkins study reveals medical errors account for 2,50,000 deaths and out of those approximately 45000 deaths are due to complicated device user interface. It is due to this it has become imperative to ensure compliance to FDA’s Human Factors guidelines compliance of medical devices.
Regulatory bodies have made it mandatory to consider human factors in their design and risk management plans. The PMA report also requires a human factors engineering report to be submitted along with other documents. Let’s dig deeper to understand what exactly do we mean by human factors and usability in medical devices.

Human Factor Considerations (Source : FDA)
What are Human Factors & Usability in Medical Devices?
Human factors: Human factors involve focusing on the interactions between people and devices. The interface, handling ease, safety and rhythm of the device with the use-environment are key aspects of human factors in medical devices.
Usability Quotient: When the device is made keeping the above aspects in mind then it’s said to have a higher usability quotient.
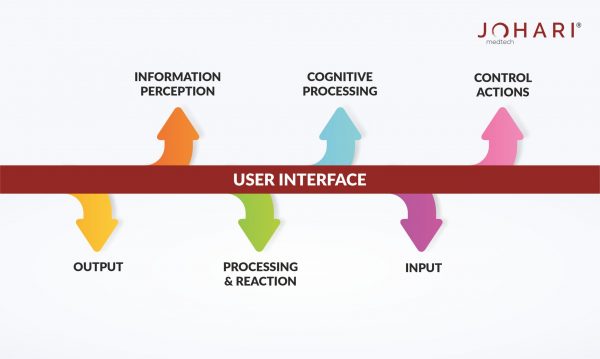
How to incorporate human factors during Medical Device Development?
Incorporating human factors in medical devices requires a few basic pre-requisites:
- What is the exact use of the medical device?
- In which environment will the device be used?
- Is the device meant for primary users or clinicians?
- What is the user demographic?
- What kind of safety will be required by the end-user for a specific type of device?
Once you have clarity on these aspects, you can proceed to next steps including:
a. User Research :User research includes testing the relevance of device for the user on multiple dimensions. The primary motive of research is to analyze the market, intent for production and safety of the end-user.
b. User Evaluation: User evaluation includes studying the user demographics to get an idea about which area will be the primary user of the device.
c. User Validation :Each of these together contribute in making a device more user-centric.
Human Factors Validation Testing
- Human factors validation testing ensures that the device is used by its intended users without any serious use errors
- Different kinds of users will have a different experience with the medical device
- The device developers must ensure that all types of users are validated for the safety
- In case the end-users won’t be given any training before using the device, the validation testing should also be done with untrained individuals
- The use environment for which the device has been created should also be kept the same during validation
Things to consider while incorporating human factors in medical device:
1. The product must adapt to the user-environment
The industrial design of the device must be done in a way that fits the end-user environment. For example a device meant for home-use must be compact and easy to carry, a device meant for OT should offer low interference and it would be better if it is wireless and battery operated. It’s highly recommended to evaluate the end-user environment before moving on to next steps.
2. The device should have intuitive interface
Accessibility covers a wide range of factors including cost, ease-of-use (interactive & comprehensible interface), and handling ease. The developers must design the product in a way that it offers all three. Missing out on any of the aspects can lead to product failure. The language, interface, and aesthetics all play a crucial role in determining success of the device.
3. Keeping it simple and relevant
One can make a product highly advanced and functionally equipped but what if the market doesn’t need it. It is important to analyze the target market well before putting money into advanced technologies. A BP Monitor with a stylish mounting cart may look relevant and stylish as a manufacturer but once, it gets into the market it is bound to fail due to contemporary irrelevance in terms of model identity and outdated aesthetics.
4. Keep the cost factor in mind
Cost is a big deal when it comes to medical devices. Refrain from adding jargon functionality and features just to increase the cost. Analyze whether the innovation you are incorporating will add some value to the device or not. If it doesn’t give the user a seamless experience, it’s irrelevant to merely increase the cost with unused features.
5. Prioritizing safety in the medical device
Medical devices deal with human lives. A minor glitch at any level can incur huge loss, to ensure that there are no errors FDA has come up with certain strict norms. These norms include:
- Strict documentation requirements including DHR, DMR and so on to enable traceability
- Ensure clinical trials of the new innovative medical devices
- Ensuring cybersecurity in medical devices
- Ensuring human factor validation testing before releasing the device for mass manufacturing
- Ensuring post-market surveillance of medical devices to incorporate safety as per the market feedback
Why is human factor engineering important to medical devices?
The core purpose behind incorporating human factors in the device is to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the device in the use environment.
A few key benefits that come with incorporating human factors in the device are:
- Easy to use devices
- Safer connections between device connections & accessories
- Easier to read controls & displays
- Better user understanding of device status & operation
- More in-depth understanding of the patient’s current medical condition
- Sound alarm signals
- Easy device maintenance & Repair
- Optimum training requirements
- Minimal to zero chances of product recalls
- Reduced risk of adverse events
At Johari we keep usability and human factors as priority at every step of the Medical Device Development & Manufacturing cycle.

