Electrical stimulation is a type of therapeutic treatment that can serve many different purposes in physical therapy. It can be used to decrease pain and inflammation, improve circulation, and it can help your muscles contract properly. Electrical stimulation often is used to augment your physical therapy program after an injury or illness.
Electrical stimulation is an incredible technology with the potential to dramatically change the way we restore and enhance the human body.
Changing times demand a more non-invasive approach to pain alleviation and elimination.
Do you know how it all begin?
Use of electricity for curing pain dates back to thousands of years back in 19th century. The use of currents in pain management is divided into several phases.
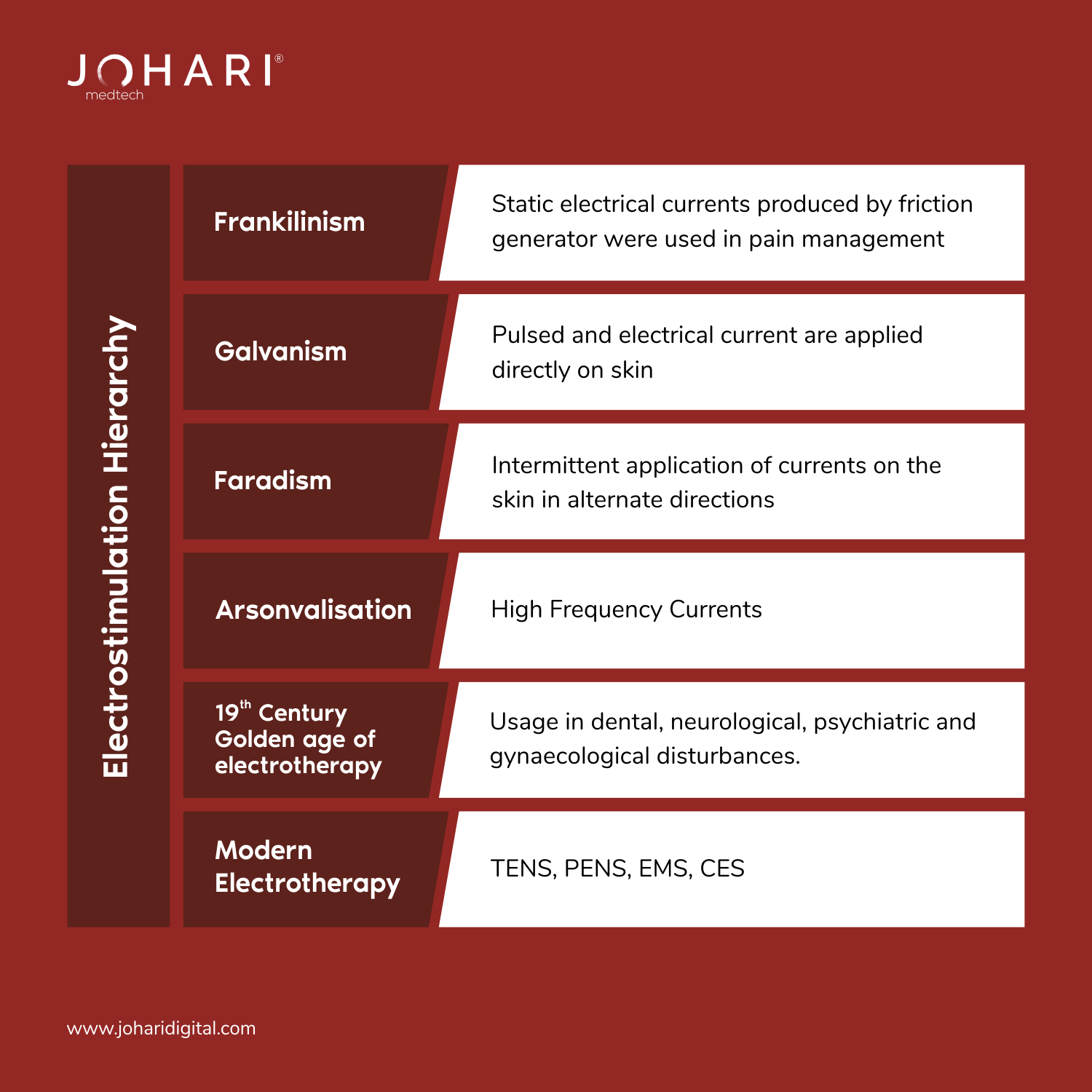
Now, you know how it all begin!
Moreover, electrical stimulation is being utilized in vast avenues to alleviate pain and eliminate stress. Physiotherapists use the different waveforms for different types of pains in physiotherapy Clinic.
This list of different types of electrical stimulation can help you understand how it is commonly used in physical therapy.
Different Types of Electrical Stimulation
-
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
- Interferential Current (IFC) Electrical Stimulation
- High Voltage Electrical Stimulation
- Electrical Muscle Stimulation
- Functional Electrical Stimulation
- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
- Russian Electrical Stimulation
- Galvanic Electrical Stimulation
- Faradic Electrical Stimulation
#1. TENS (Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation)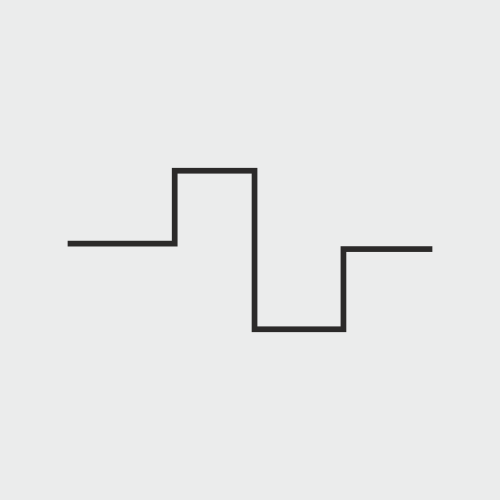
Transcutaneous electrical muscle stimulation is the oldest form of muscle stimulation used for pain relief. It is the most pervasive form of electrical stimulation. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a therapy that uses low voltage electrical current to provide pain relief. A TENS unit consists of a battery-powered device that delivers electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the surface of your skin. The electrodes are placed at or near nerves where the pain is located or at trigger points.
Indications
-
- Arthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Knee pain
- Back pain
- Neck pain
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Pelvic pain from periods or endometriosis
Example: Stimtec2
#2. Interferential Current (IFC) Electrical Stimulation
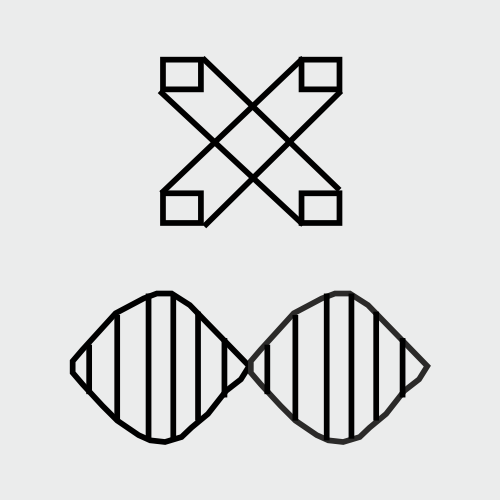 Interferential therapy utilizes two medium frequencies in a manner that does not cause any major side effects. The interferential stimulation is the same as low-frequency treatment. The sensation induced by IFT will vary according to the different AMF settings. The lower AMF generates a tapping or beating sensation while the higher AMF generates a buzzing or tingling sensation. Approximately 10 – 15 minutes are needed to properly deliver the impact of the IFT in the affected area.
Interferential therapy utilizes two medium frequencies in a manner that does not cause any major side effects. The interferential stimulation is the same as low-frequency treatment. The sensation induced by IFT will vary according to the different AMF settings. The lower AMF generates a tapping or beating sensation while the higher AMF generates a buzzing or tingling sensation. Approximately 10 – 15 minutes are needed to properly deliver the impact of the IFT in the affected area.
Indications
- Muscle spasm
- Edema
- Hematoma
- Chronic ligament lesion
- Radiculopathy
- Stress incontinence
- Chronic ligament lesion
Example : Stim3
#3. High Voltage Electrical Stimulation
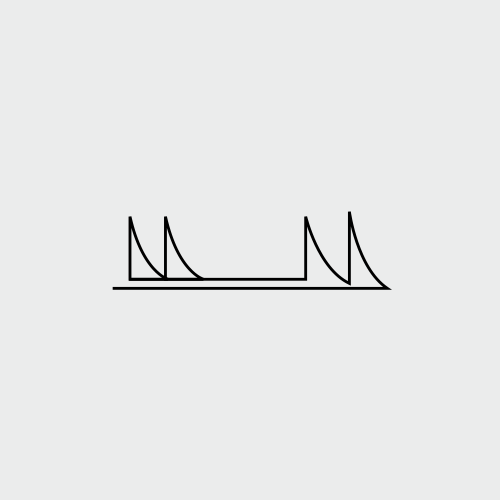 A type of electrical stimulation essentially involved in deep wound healing. The process of electrical stimulation improves the healing time up to three times. The electrical stimulation process in high voltage range improves the blood flow and replaces the lost cells. This creates a completely new area for healing and processing.
A type of electrical stimulation essentially involved in deep wound healing. The process of electrical stimulation improves the healing time up to three times. The electrical stimulation process in high voltage range improves the blood flow and replaces the lost cells. This creates a completely new area for healing and processing.
Indications
-
- Adhesive bursitis
- Wound healing
- Cervical sprain
- Degenerative Disc
- Epicondylitis
- Sprain
- Post-operative pain
Example: Anagesic Pulser 439 Plus
#4. Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
EMS (Electrical muscle stimulation) is primarily used in facial muscle stimulation. Also, largely in cases involving neurological disorders like Bell’s Palsy, this type of stimulation is highly effective in overcoming similar disorders.
Electrical stimulation is a new-age technique to facilitate pain and stress relief without compromising the body’s metabolism. It is highly effective in muscle strengthening and conditioning. Electrical stimulation is also highly effective in weight management.
Indications
-
- Physical rehabilitation
- Weight loss
- Muscle spasm relaxation
- Restore the functionality loss
- Atrophy
Example : NMS-498
#5. Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Low electric currents required for creating sensations that stimulate body to restore lost functionality is FES. In cases of absolute paralysis or lost functionality FES is of highly great value. It is highly important for people who have lost the capability to walk or move. The stimulation helps in gaining a certain level of bowel and bladder function. In cases when a person cannot perform general functions like breathing, grasping, transferring, standing or walking FES plays a very important role.
Indications
-
- Regaining the lost functionality.
- In paralysis
- Lost muscle functionality
#6. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation is applied to a group of muscles. Here the repetitive contractions help in retrieving the lost functionality. This treatment is very crucial for retraining and strengthening the weak urinary muscles.
Indications
-
- Incontinence
- Muscle rehabilitation
- Muscle weakness
- Neuromuscular re-education
#7. Russian Electrical Stimulation
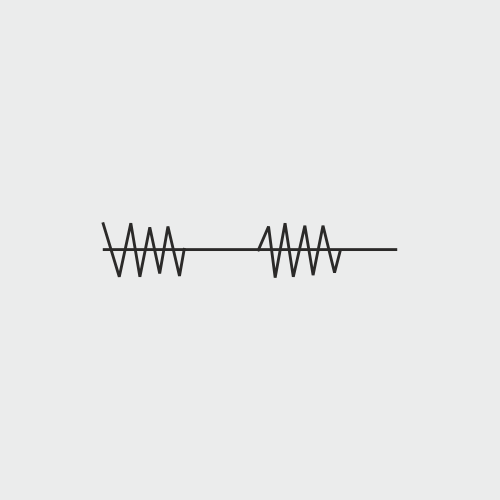 The Russian current modality is a medium frequency current generally used for strengthening and muscle re-education. The current is applied in alternating pulsed or burst mode. A study published in the International Journal of Rehabilitation and Science reveals that Russian current is highly effective in improving the quadriceps strength in burn patients.
The Russian current modality is a medium frequency current generally used for strengthening and muscle re-education. The current is applied in alternating pulsed or burst mode. A study published in the International Journal of Rehabilitation and Science reveals that Russian current is highly effective in improving the quadriceps strength in burn patients.
Indications
-
- Muscle Strengthening
- Muscle re-education
- Quadriceps strengthening
#8. Galvanic Electrical Stimulation
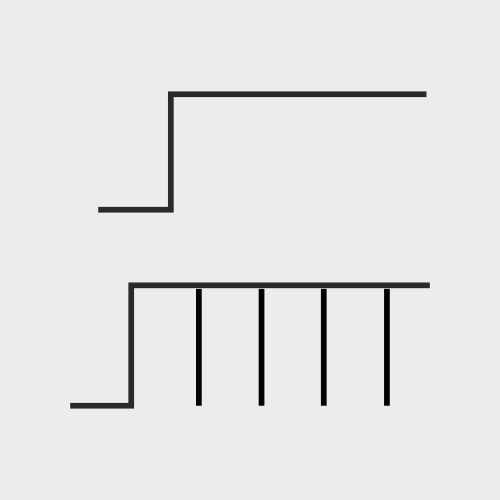 An interrupted direct current is commonly used in the frequency of 30 pulses/min. In case when the duration has increased the frequency of the current must be reduced. The galvanic current works on the neural endings such that the cathode electrode enhances the sensitivity of nerves and the anode diminishes the pain. The process involves disruption of the signals of pain to alleviate or eliminate pain. These act on the denervated muscle to produce the effect.
An interrupted direct current is commonly used in the frequency of 30 pulses/min. In case when the duration has increased the frequency of the current must be reduced. The galvanic current works on the neural endings such that the cathode electrode enhances the sensitivity of nerves and the anode diminishes the pain. The process involves disruption of the signals of pain to alleviate or eliminate pain. These act on the denervated muscle to produce the effect.
Indications
-
- Axonotmesis
- Neurotmesis
- Improving skin elasticity
- Minimizing fine lines and wrinkles
- Boosting blood circulation & oxygen levels in the skin
#9. Faradic Electrical Stimulation
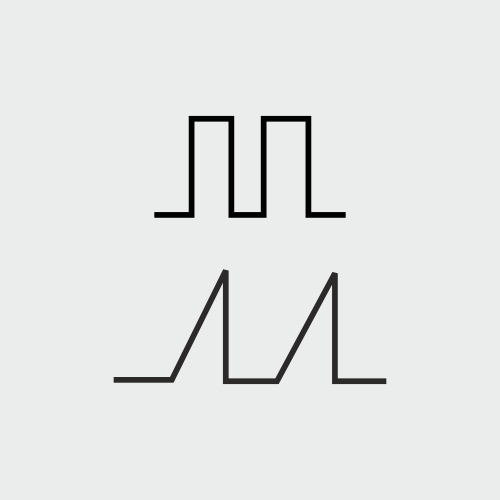 An interrupted direct current with a frequency of 50-100Hz with a pulse duration ranging from 0.1 -1 Ms. Highly effective in innervated muscles and feels like a prickling sensation while application. The stimulation causes a reaction in the motor nerves of the application area. Faradic acts on innervated muscles which differentiate it from galvanic in terms of physiological effect.
An interrupted direct current with a frequency of 50-100Hz with a pulse duration ranging from 0.1 -1 Ms. Highly effective in innervated muscles and feels like a prickling sensation while application. The stimulation causes a reaction in the motor nerves of the application area. Faradic acts on innervated muscles which differentiate it from galvanic in terms of physiological effect.
Indications
-
- Muscle re-education
- Pain relief in knee syndrome
- Muscle atrophy
- Restoration of nutrient blood flow in the area treated.


Very Well explained all the waveforms of electrical stimulation. Keep on sharing the valuable information
Great article!
Highly informative!
Which is a good one to buy
Thanks for highly informative 🙏
TENS stops the excessive urge to move limbs during episodes of restless leg syndrome